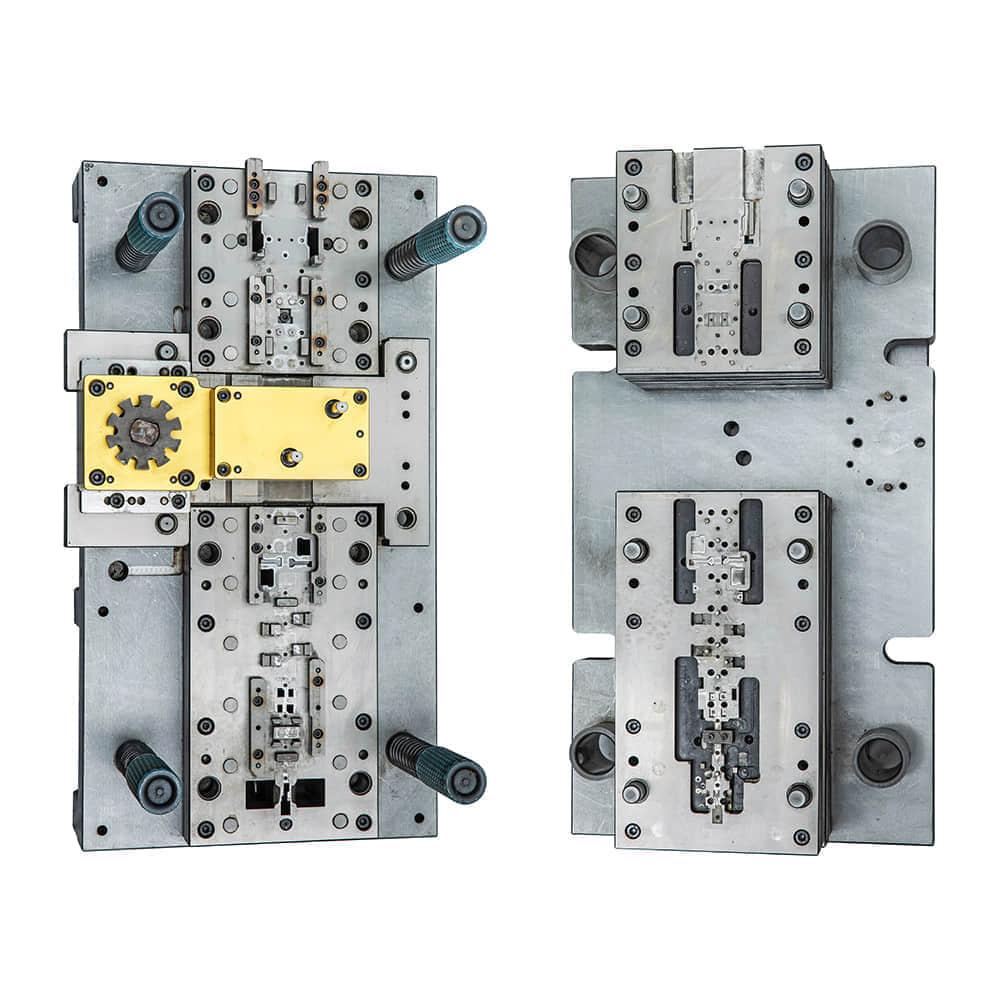
Metal stamping die, often referred to simply as a “die,” is a fundamental tool in the world of metalworking and manufacturing. It plays a crucial role in shaping metal sheets and components with precision and consistency. In this article, we will delve into the world of metal stamping dies, exploring their significance, design, and the industries they serve.
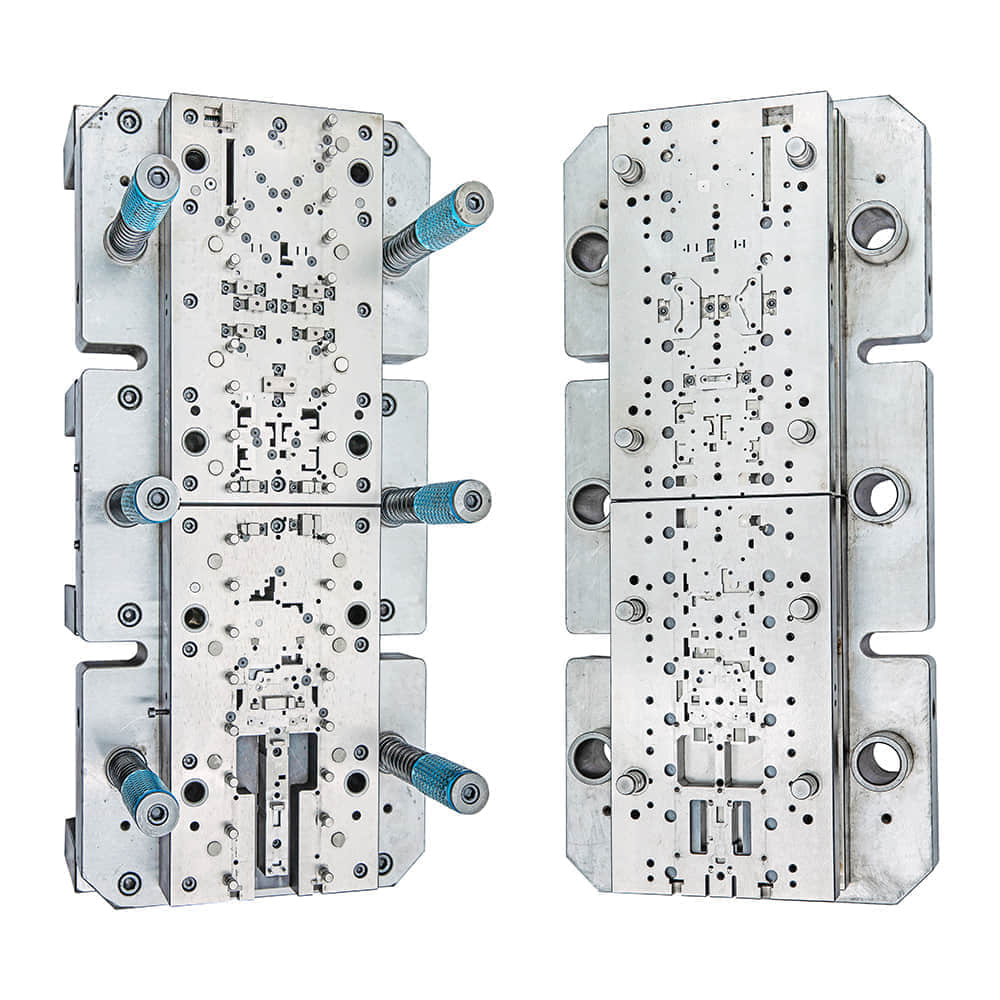
The Significance of Metal Stamping Dies
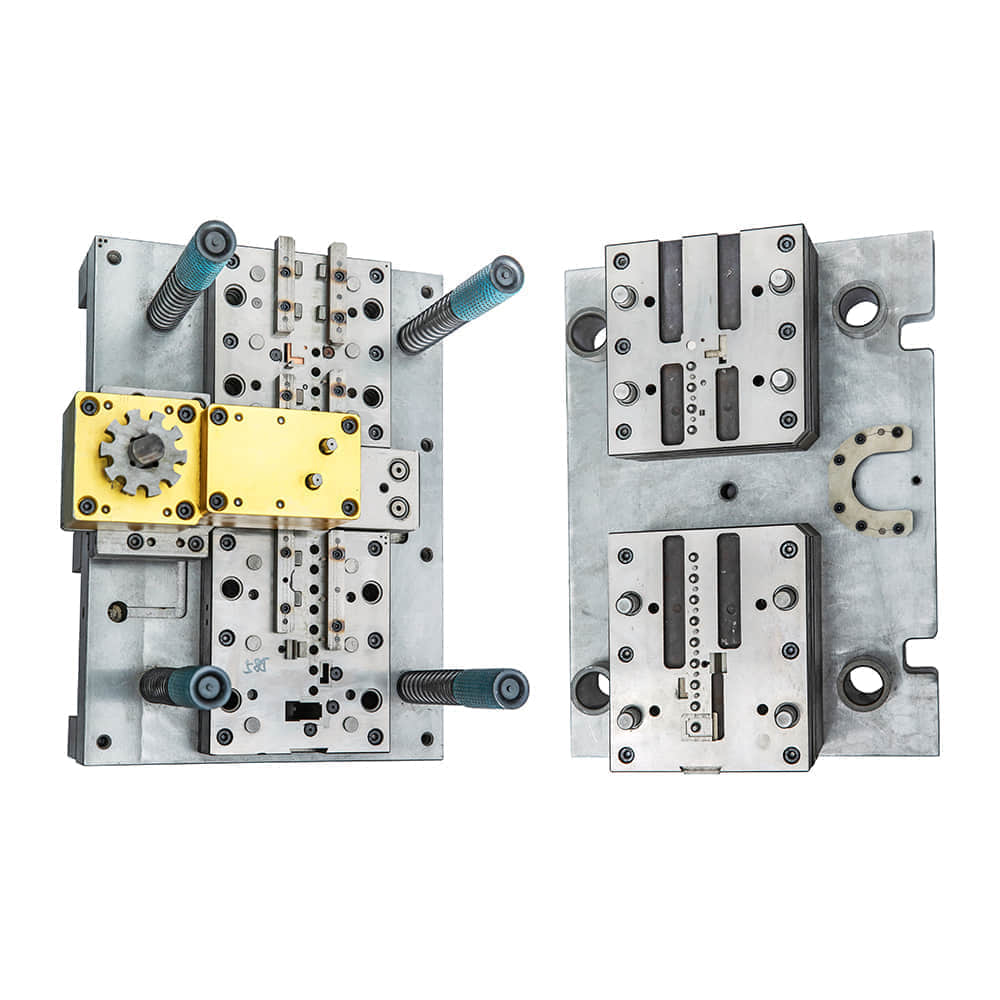
Metal stamping dies are essential in the fabrication of a wide range of metal products, from automotive components to household appliances and electronics. They enable manufacturers to transform flat metal sheets or coils into intricate shapes, meeting the strictest tolerances and quality standards. One of the primary advantages of metal stamping dies is their ability to produce identical parts rapidly. This uniformity is critical in industries where product consistency and quality are paramount. Whether it’s creating intricate car body panels or simple metal brackets, stamping dies ensure that each part meets the same exact specifications, minimizing errors and defects. Designing Metal Stamping Dies The design of a metal stamping die is a meticulous and highly specialized process that requires a deep understanding of the intended product, materials, and manufacturing techniques. Several key elements must be considered during the design phase: Material Selection: The choice of material for the die itself is vital. Dies are often made from high-quality tool steel, which can withstand the immense pressure and wear associated with the stamping process. Die Components: Dies are typically composed of two main components: the male die (punch) and the female die (die cavity). These components work together to shape the metal. The punch exerts force on the metal, while the die cavity provides the desired shape. Tolerance and Precision: Designers must calculate and specify the exact tolerances required for the stamped parts. These tolerances ensure that the finished products meet the desired specifications. Durability: To maximize the lifespan of a stamping die, it must be designed to withstand the repetitive stresses and forces it will encounter during production. Heat treatment and surface coatings can enhance durability. Maintenance Considerations: Die designers also need to think about ease of maintenance and repair. Well-designed dies should be relatively simple to disassemble and reassemble for maintenance purposes. Industries and Applications Metal stamping dies find applications in a wide variety of industries, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, and consumer goods. Here are a few examples of how metal stamping dies are used: Automotive Industry: Metal stamping dies are extensively employed to manufacture car body panels, chassis components, and engine parts. The automotive sector relies heavily on the precision and efficiency of stamping processes. Aerospace Industry: In aerospace manufacturing, where safety and precision are paramount, stamping dies are used to create aircraft structural components, including brackets, frames, and engine parts. Electronics Industry: Precision is crucial in electronic devices, and metal stamping dies help produce intricate components like connectors, brackets, and enclosures. Consumer Goods: Everyday products like kitchen appliances, home electronics, and furniture often incorporate stamped metal parts. Stamping dies ensure the consistency and quality of these products. In conclusion, metal stamping dies are the unsung heroes of the manufacturing world, enabling the creation of countless products we rely on daily. Their precision and reliability are essential for industries that demand consistency and quality in their end products. As technology advances, so too will the design and capabilities of metal stamping dies, ensuring their continued importance in the world of manufacturing.