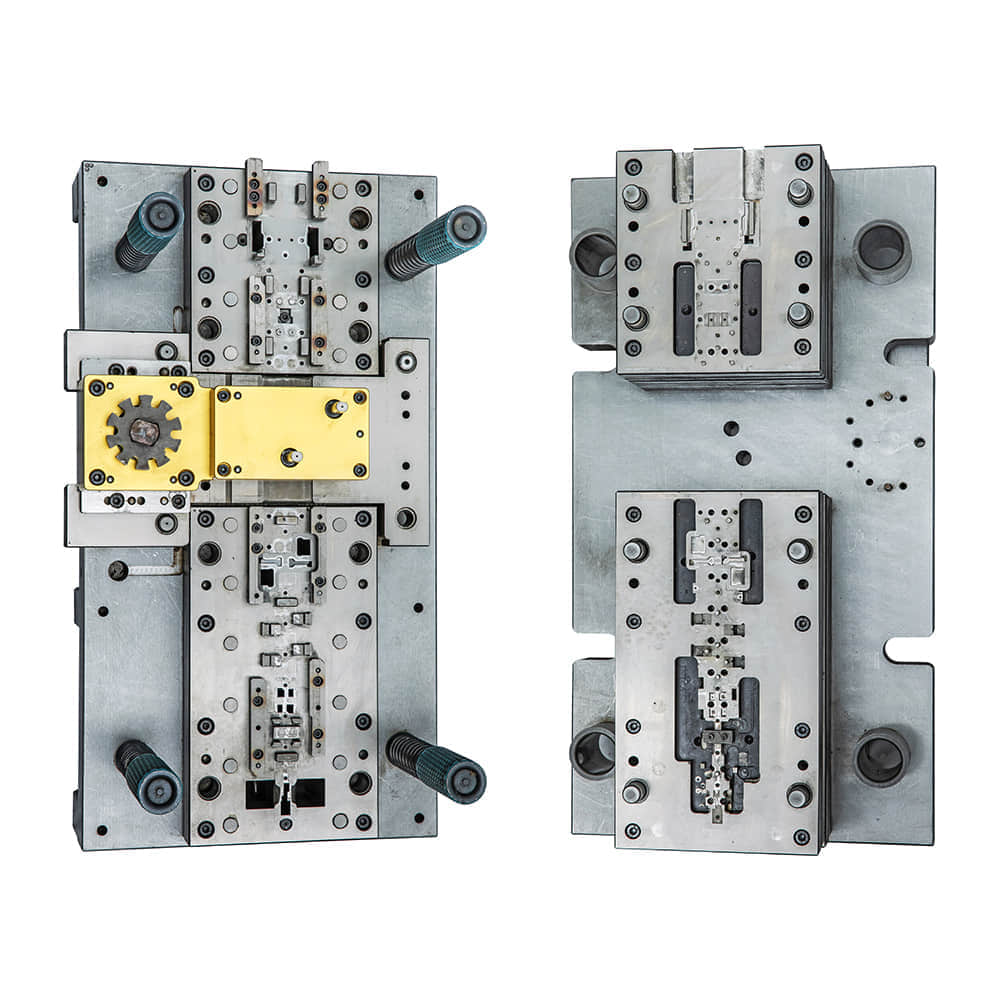
Blanking dies are critical tools in the field of metalworking and fabrication. They play a fundamental role in the process of creating precision-cut metal blanks, which are the building blocks for a wide range of products in various industries. In this article, we will delve into the world of blanking dies, exploring their types, components, applications, and the key factors that influence their design and performance.
Types of Blanking Dies
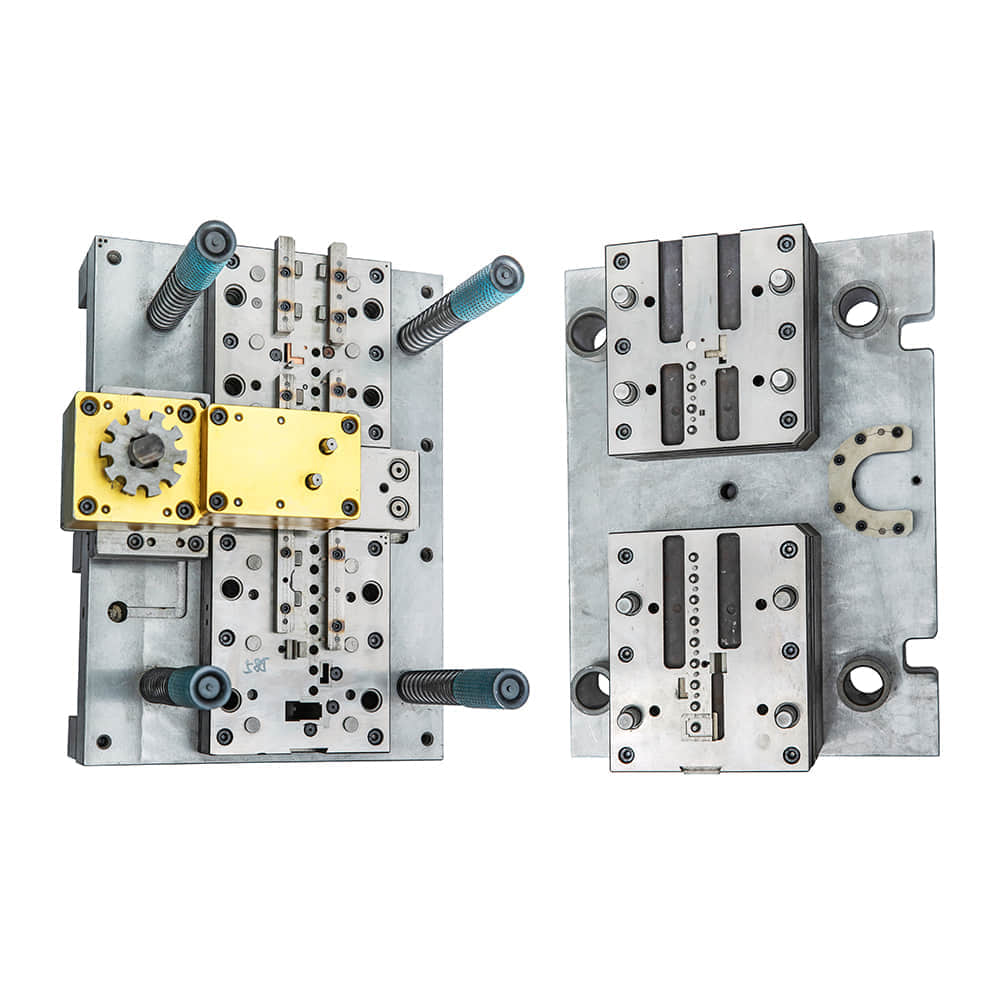
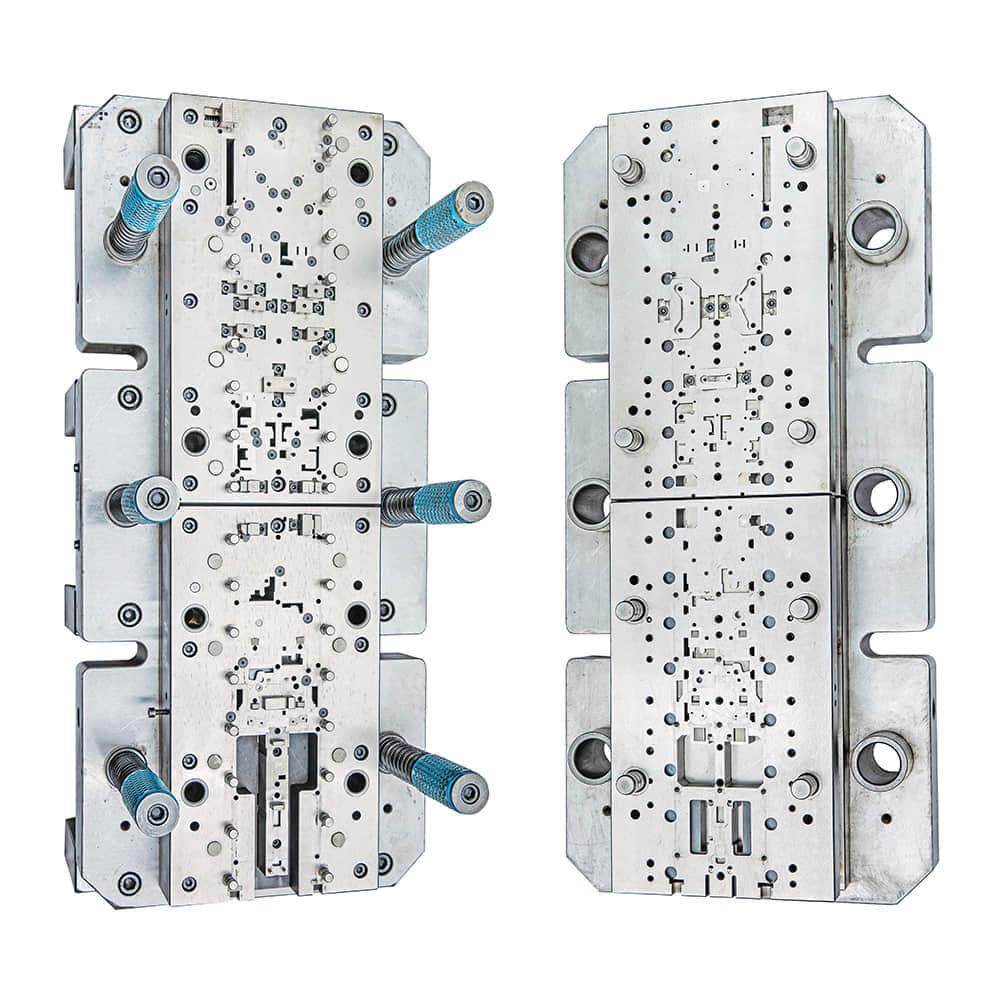
Blanking dies come in various forms, each designed for specific applications. The two primary types of blanking dies are: 1. Compound Blanking Die:This type of die is used when the blank requires multiple operations, such as piercing, notching, or bending, in addition to the blanking process itself. Compound blanking dies are versatile and can produce complex shapes. 2. Progressive Blanking Die:Progressive dies are designed for high-speed production of simple, repetitive blanks. They consist of multiple stations, each performing a specific operation, with the material moving through the die in a step-by-step fashion. Progressive dies are ideal for large-scale manufacturing. Components of a Blanking Die A typical blanking die consists of several key components: 1. Die Block:The die block is the main body of the die and provides the structural support for the other components. It contains the die cavity, which determines the shape of the blank. 2. Punch:The punch is a hardened steel tool that descends into the die cavity to cut the material and form the blank. 3. Stripper Plate:The stripper plate holds the material in place during the blanking process and prevents it from sticking to the punch. 4. Pilot Pin:The pilot pin ensures precise alignment of the material with the die cavity. 5. Guide Pins and Bushings:These components maintain the proper alignment of the punch and die block. 6. Shearing Clearance:This is the gap between the punch and the die block. It determines the quality of the cut and is critical for preventing excessive tool wear. Applications of Blanking Dies Blanking dies find applications in various industries, including automotive, electronics, aerospace, and consumer goods manufacturing. Some common applications include: 1. Automotive Industry:Blanking dies are used to produce a wide range of automotive components, such as body panels, brackets, and gears. 2. Electronics Industry:In the electronics sector, blanking dies are used to manufacture intricate components like connectors and contacts. 3. Aerospace Industry:Blankings dies are employed in the production of aerospace parts, including engine components and structural elements. 4. Consumer Goods:Items such as kitchen utensils, appliances, and decorative metal pieces are often produced using blanking dies. Factors Influencing Die Design and Performance The design and performance of blanking dies are influenced by several factors: 1. Material Type:Different materials require different die configurations. Harder materials may require more robust dies and increased shearing clearance. 2. Material Thickness:Thicker materials demand stronger and more durable dies to withstand the cutting forces. 3. Blank Shape and Size:The complexity and dimensions of the blank determine the die’s design and the type of die (compound or progressive) to be used. 4. Production Volume:High-volume production may necessitate the use of progressive dies for efficiency. 5. Tool Material and Heat Treatment:The choice of tool material and heat treatment methods significantly impacts die durability and performance. In conclusion, blanking dies are essential tools in the metalworking and fabrication industries, serving a wide range of applications. Understanding the types, components, and factors influencing their design and performance is crucial for achieving high-quality and cost-effective production in various manufacturing processes. Whether you’re producing automotive parts, electronic components, or consumer goods, blanking dies are a fundamental part of the manufacturing toolkit.