Metal stamping is a versatile and widely used manufacturing process that plays a crucial role in various industries. It involves transforming flat metal sheets into desired shapes and sizes through a combination of cutting, bending, and forming techniques. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of metal stamping parts, exploring its applications, benefits, and the key processes involved.
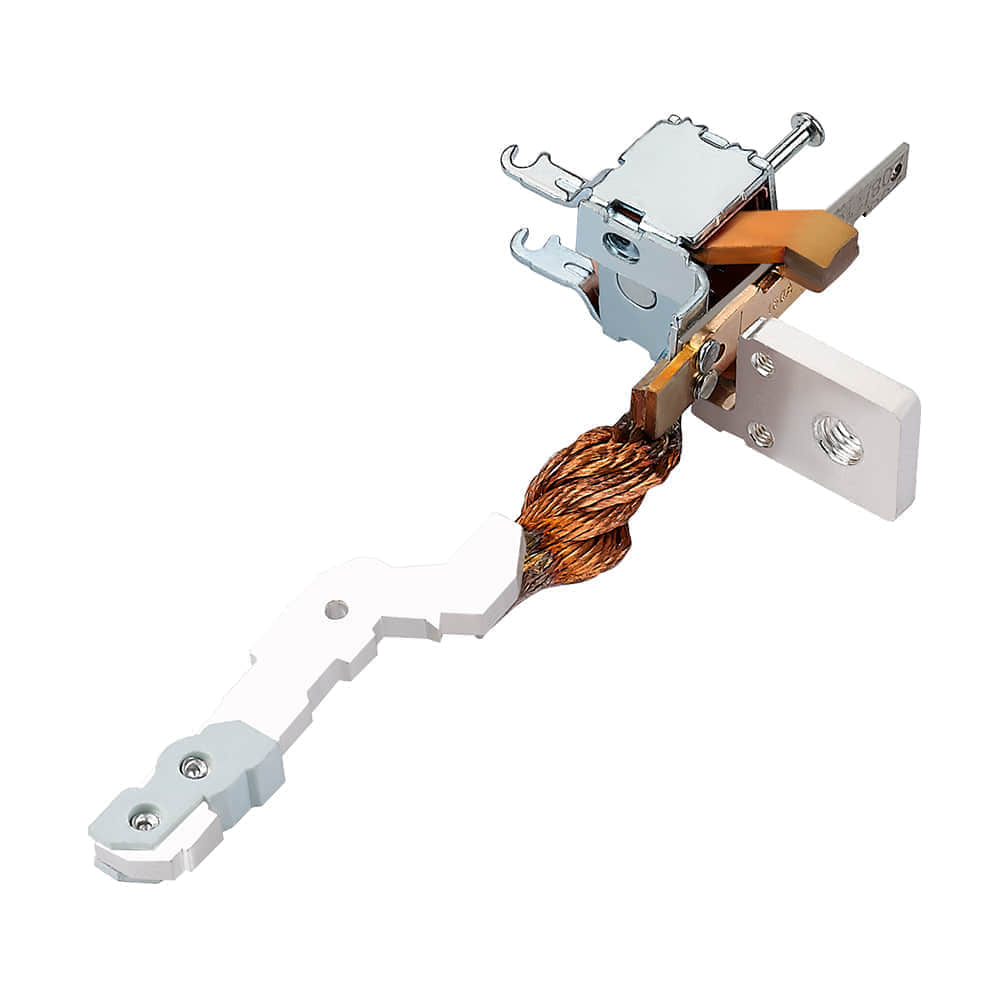

1. Applications of Metal Stamping Parts
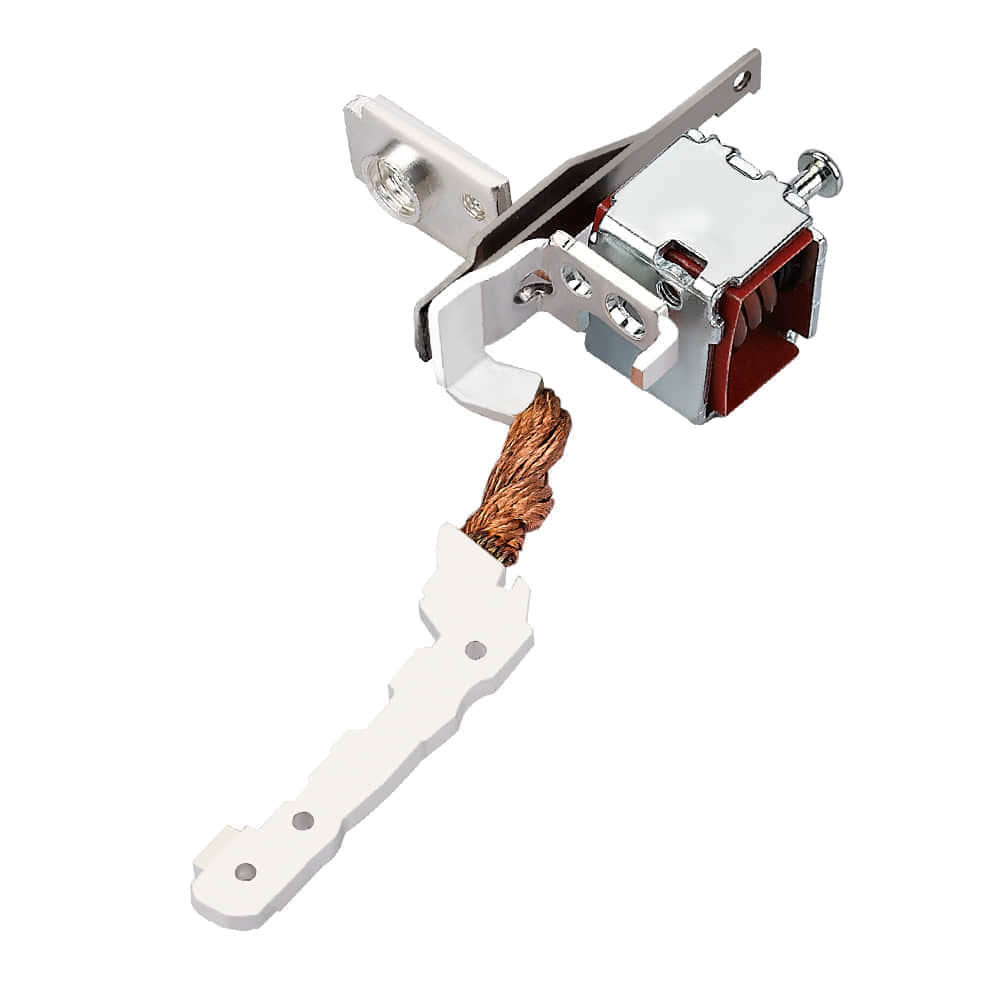

Metal stamping parts find applications in an array of industries, ranging from automotive and aerospace to electronics and consumer goods. Here are some common uses: 1.1 Automotive IndustryIn the automotive sector, metal stamping is utilized to manufacture a wide range of components, including body panels, brackets, hinges, and structural parts. The process ensures precision and durability, making vehicles safer and more reliable. 1.2 Electronics and AppliancesMetal stamping is essential in producing various components for electronics and appliances, such as connectors, brackets, and heat sinks. These precision parts are crucial for the functionality and longevity of these devices. 1.3 Aerospace IndustryIn aerospace, metal stamping is employed to create lightweight yet robust components like aircraft frames, engine parts, and brackets. The high precision achieved through stamping is vital for ensuring the safety of air travel. 1.4 Medical EquipmentThe medical industry relies on metal stamping for the fabrication of surgical instruments, implants, and diagnostic equipment. The biocompatible materials used in stamping ensure the safety and reliability of these critical devices. 2. Benefits of Metal Stamping Parts 2.1 Cost-EfficiencyMetal stamping is a cost-effective manufacturing method, as it allows for the rapid production of complex parts in large quantities. This efficiency reduces labor costs and leads to competitive pricing. 2.2 Precision and ConsistencyStamping provides unparalleled precision and consistency, ensuring that each part meets exact specifications. This is crucial in industries where safety and reliability are paramount. 2.3 VersatilityMetal stamping can work with a wide range of materials, including steel, aluminum, copper, and brass. This versatility enables manufacturers to choose the right material for their specific application. 2.4 Reduced WasteThe process generates minimal waste, as it optimizes material usage by cutting and forming parts from flat sheets. This aligns with the principles of sustainability and environmental responsibility. 3. Key Processes in Metal Stamping 3.1 BlankingBlanking is the first step in metal stamping, where a flat metal sheet is cut into a specific shape. This process creates a flat piece known as a “blank” that serves as the starting point for further stamping operations. 3.2 BendingBending involves shaping the blank by applying force to specific areas, typically using a punch and die. This process creates the desired angles and curves in the metal. 3.3 FormingForming is the process of stretching or compressing the metal to achieve the desired shape. This can involve deep drawing, where the blank is gradually pushed into a die cavity to create complex shapes. 3.4 PiercingPiercing is used to create holes or cutouts in the metal component. It is often done simultaneously with other stamping operations to minimize material waste. 3.5 CoiningCoining is a precision stamping process used to improve the part’s surface finish and dimensional accuracy. It involves high-pressure compression of the metal between the punch and die. In conclusion, metal stamping parts are integral to numerous industries, offering cost-efficient, precise, and versatile solutions for manufacturing complex components. Understanding the applications, benefits, and key processes of metal stamping is essential for businesses seeking to leverage this efficient manufacturing technique in their operations. Metal stamping’s continued evolution and innovation ensure that it will remain a cornerstone of modern manufacturing for years to come.