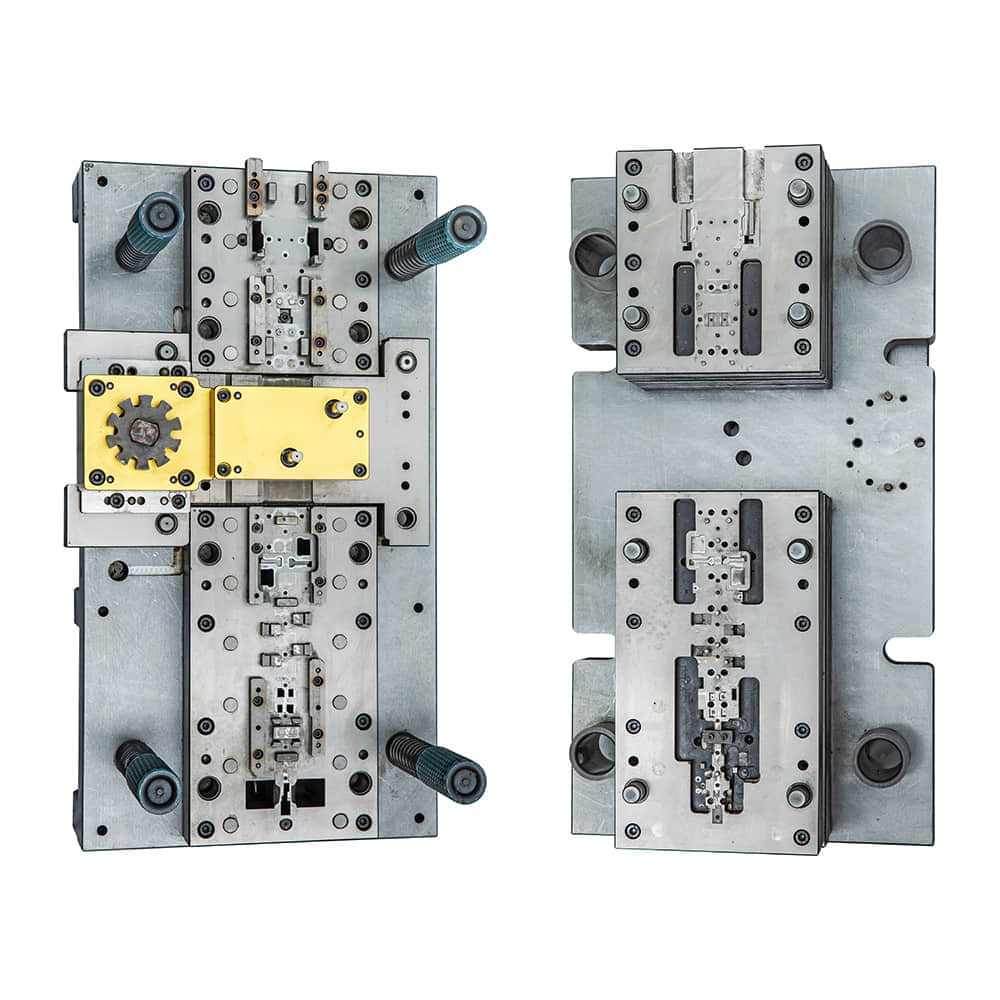
Progressive Die: Streamlining Manufacturing Processes for Efficiency and Precision
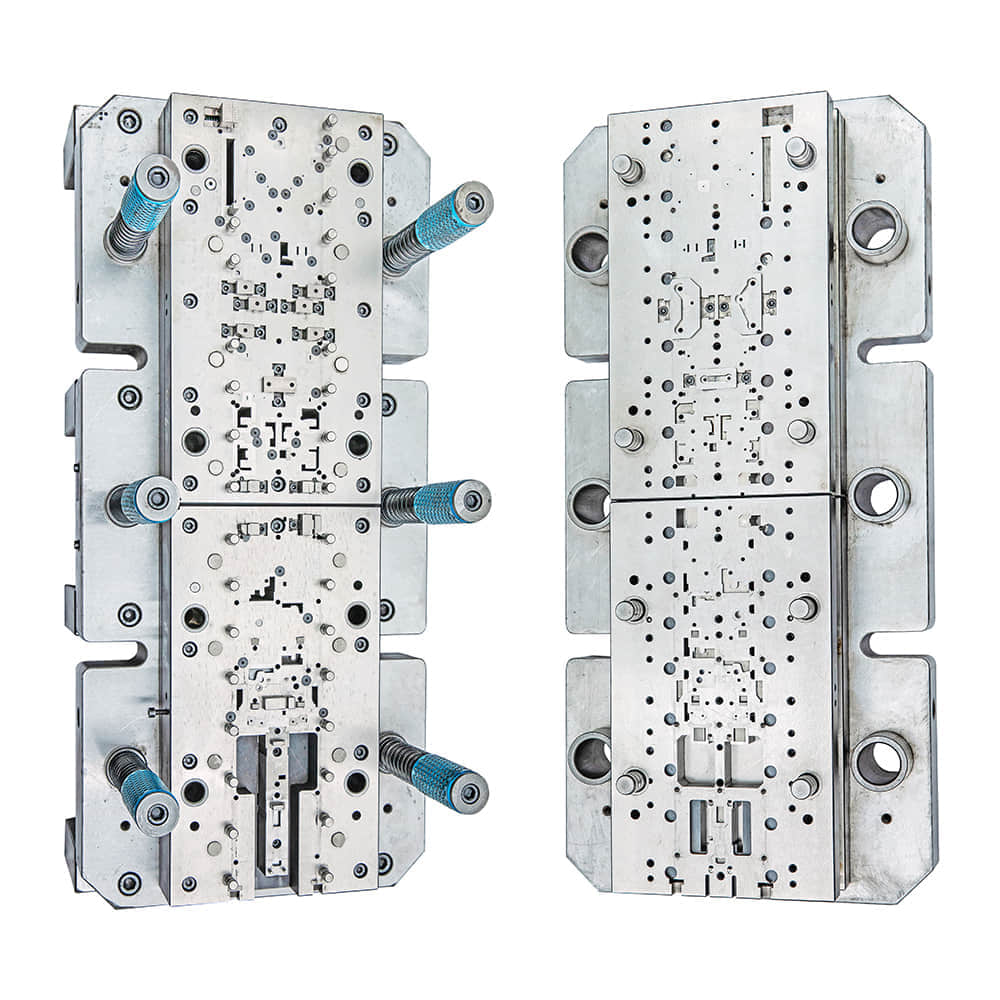
In the dynamic landscape of modern manufacturing, efficiency and precision are paramount to success. One innovative tool that has revolutionized the way complex parts are produced is the progressive die. With its ability to transform raw materials into intricate components with unparalleled speed and accuracy, the progressive die plays a crucial role in various industries.
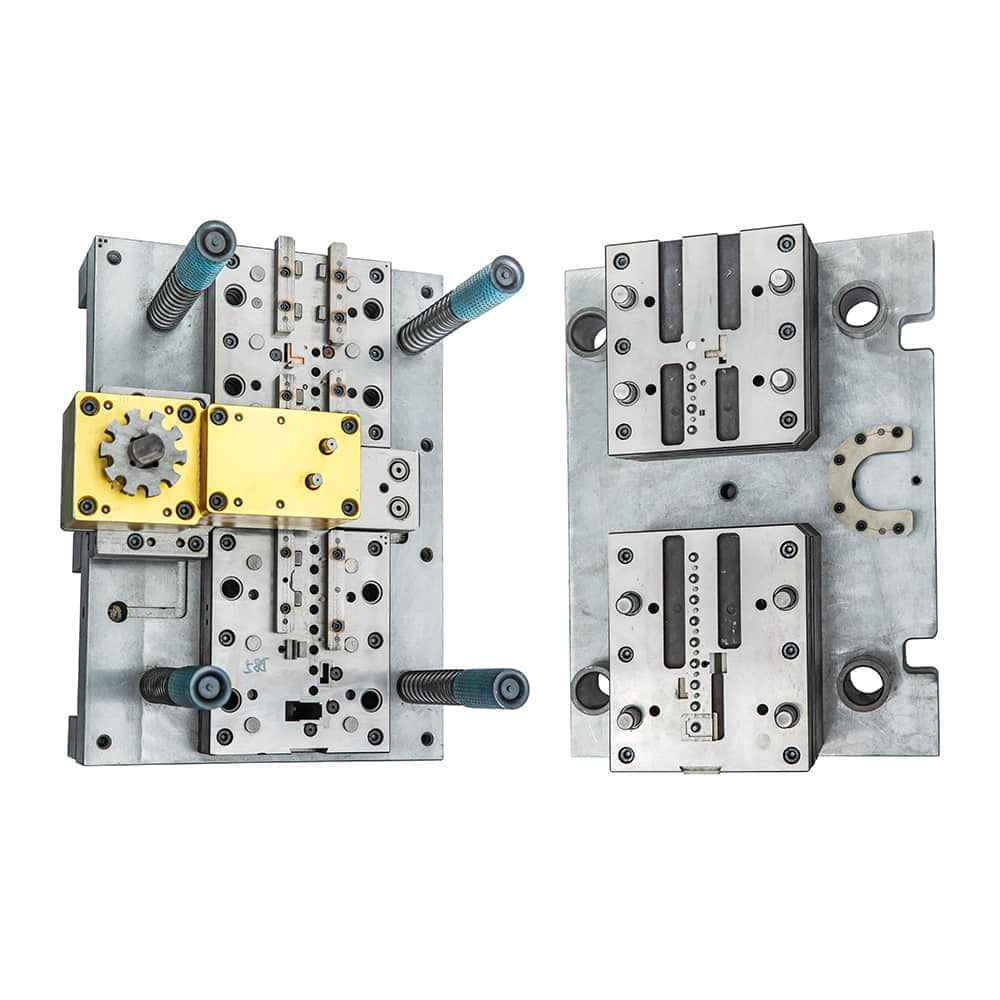
A progressive die is a specialized tool used in stamping and forming processes to produce intricate parts from sheet metal and other materials. Unlike traditional methods that require multiple operations and tools, the progressive die integrates numerous tasks into a single, automated process. The die is composed of a series of interconnected stations, each performing a specific operation on the material as it moves through the machine. This seamless integration not only accelerates the production cycle but also ensures consistency and uniformity in the final products. One of the most significant advantages of using a progressive die is its efficiency. The continuous flow of material through the die eliminates the need for manual intervention between each operation, significantly reducing the production time. Additionally, the automated nature of the process minimizes the risk of errors that could arise from repetitive tasks, ensuring a higher level of precision and quality in the end products. The progressive die’s ability to create complex parts with tight tolerances is another noteworthy feature. As the material advances through the die stations, each operation refines the part further. This incremental refinement allows manufacturers to achieve intricate designs and dimensions that might be unattainable through traditional manufacturing methods. Whether it’s producing intricate electronic components or intricate automotive parts, the progressive die excels in delivering results that meet the most demanding specifications. Industries such as automotive, electronics, aerospace, and appliance manufacturing have all benefited immensely from the progressive die technology. In the automotive sector, for instance, the progressive die is responsible for producing components like brackets, connectors, and clips, which are essential for the assembly of vehicles. The precision and speed of the process have contributed to faster production cycles, reduced lead times, and ultimately, cost savings. Moreover, the progressive die’s environmental impact cannot be ignored. The efficiency of the process translates into optimized material usage, reducing waste generation. The automated nature of the operations also ensures a safer working environment by minimizing the need for manual handling of materials during production. As sustainability becomes a growing concern in the manufacturing industry, the progressive die aligns perfectly with the goals of minimizing waste and energy consumption. However, implementing a progressive die system requires careful consideration and expertise. The design of the die, the selection of materials, and the coordination of various stations demand a high level of engineering knowledge. Moreover, regular maintenance is essential to keep the die in optimal working condition. Any deviation or malfunction in the die’s intricate components could lead to defects in the produced parts and disrupt the entire manufacturing process. In conclusion, the progressive die has emerged as a game-changer in the manufacturing world, offering a streamlined approach to producing complex and precise parts. Its ability to integrate multiple operations, enhance efficiency, and ensure precision has made it a staple in industries that demand high-quality components. As technology continues to evolve, the progressive die is likely to evolve as well, incorporating advanced materials, sensors, and automation to further enhance its capabilities. With the promise of faster production, reduced costs, and superior products, the progressive die remains an indispensable tool in the arsenal of modern manufacturers.