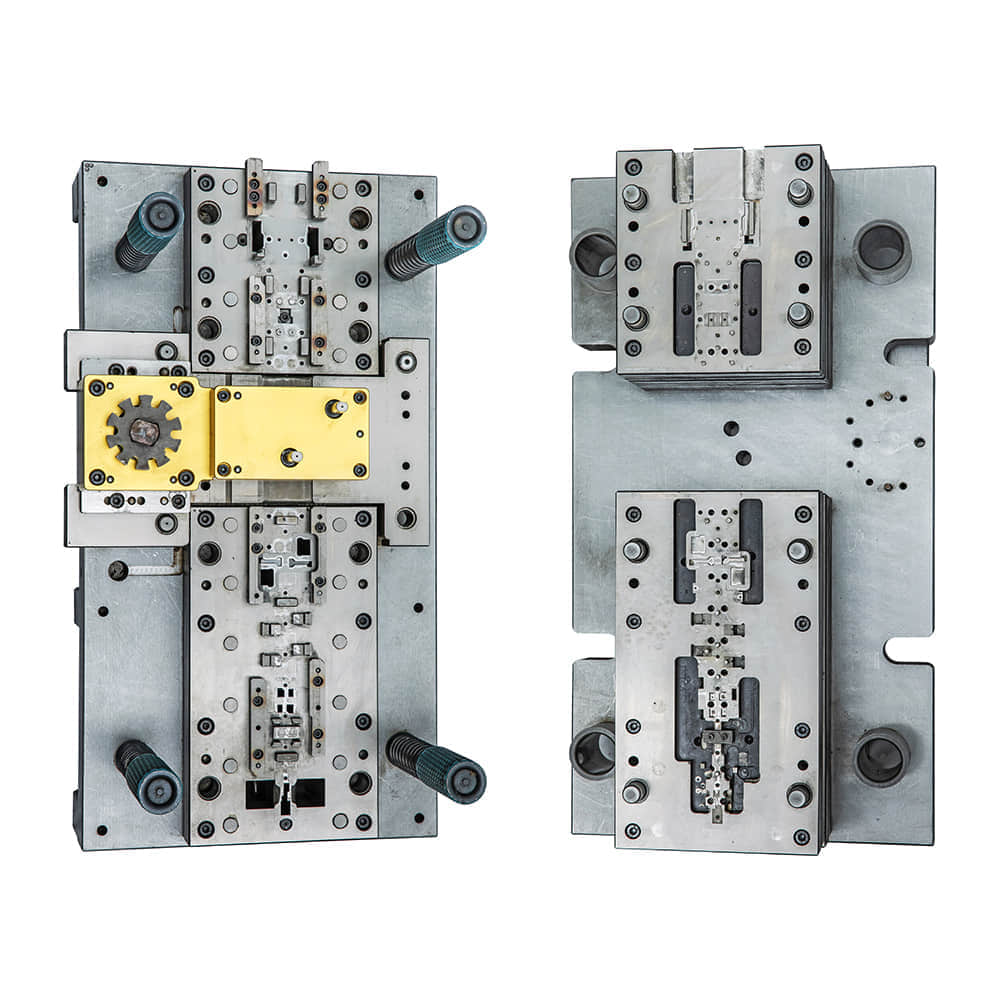
Metal stamping die, a fundamental tool in the world of manufacturing, is a testament to the fusion of artistry and science. It embodies the craftsmanship required to transform raw metal into intricate and precise components used in a multitude of industries. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating realm of metal stamping die, exploring its evolution, working principles, and the pivotal role it plays in modern manufacturing processes.
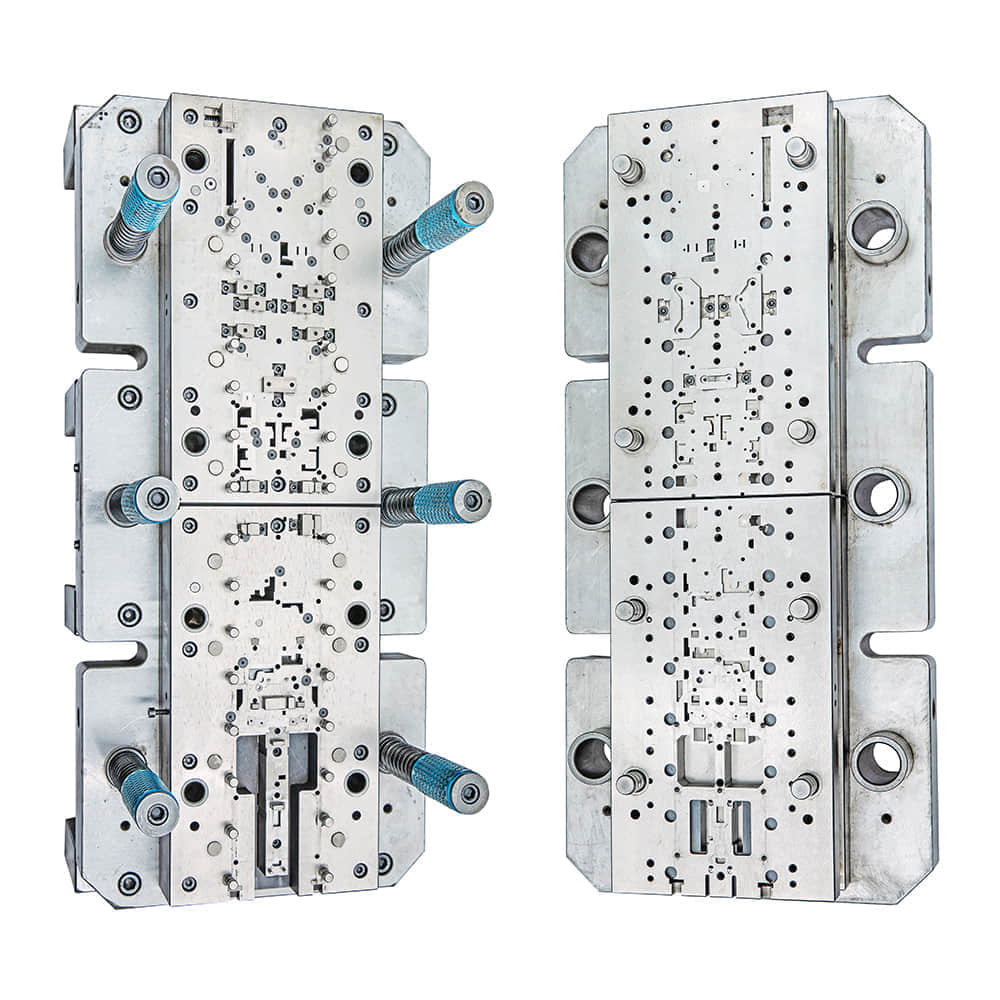
The Evolution of Metal Stamping Die
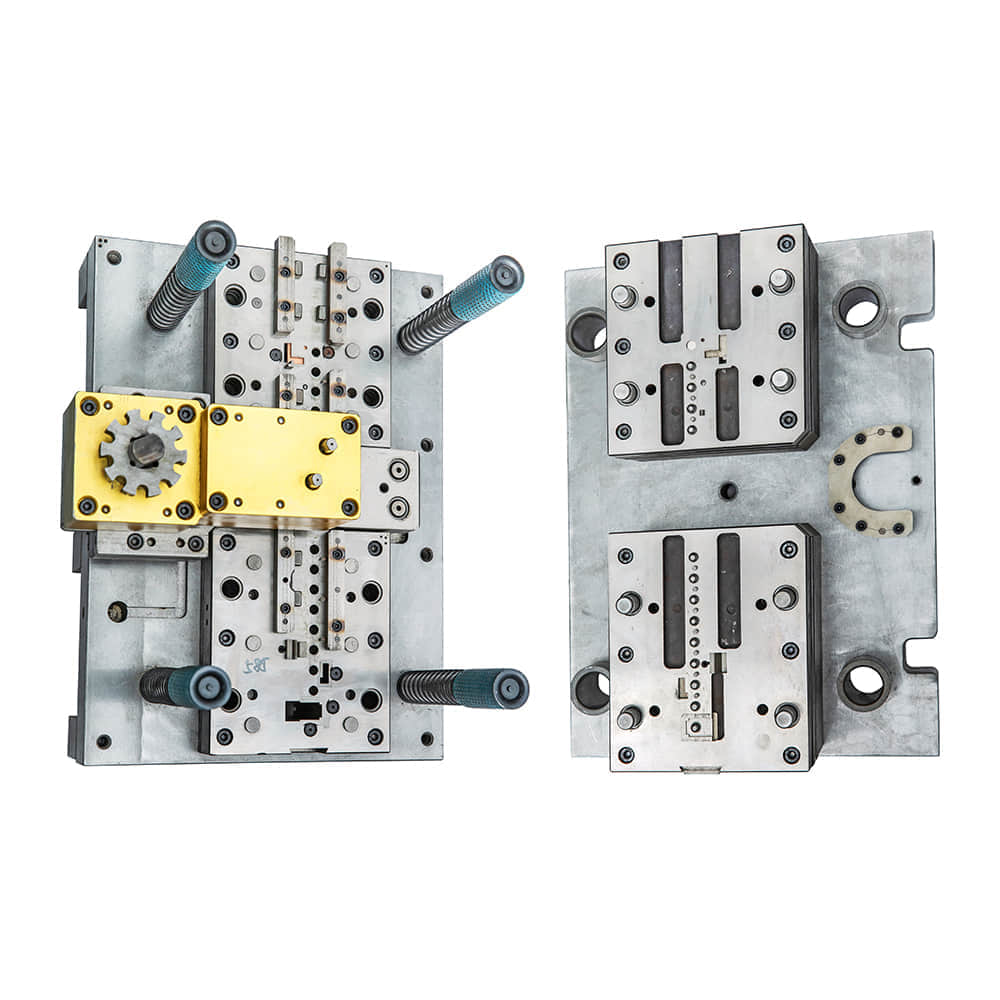
The origins of metal stamping can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where craftsmen used rudimentary tools to create simple metal shapes. Over the centuries, this art form evolved into a highly sophisticated and precise manufacturing process. The development of metal stamping die, a specialized tool designed for mass production, marked a significant turning point in the history of metalworking. The earliest metal stamping dies were handcrafted, often by skilled blacksmiths. These dies were used to create basic shapes, such as coins and simple jewelry. As industrialization spread, the demand for more complex and precise components grew, leading to the development of automated stamping machines and increasingly intricate dies. The Working Principles of Metal Stamping Die Metal stamping die operates on a deceptively simple principle: the transformation of a flat metal sheet or coil into a desired shape through the application of force. However, the execution of this principle involves a delicate interplay of factors and processes. Design and Engineering: The first step in creating a metal stamping die is meticulous design and engineering. This phase involves defining the shape of the final product, selecting the appropriate metal material, and designing the die components to ensure accuracy and longevity. Material Preparation: Metal sheets or coils are carefully selected and prepared for stamping. This includes cutting the material to the required size and often applying a lubricant to facilitate the stamping process. Stamping Process: The prepared metal material is placed into the stamping machine, where it is secured between the die and the press. The press then exerts immense force, causing the metal to conform to the shape of the die cavities. This can involve multiple stages of stamping to achieve the final shape. Quality Control: Precision is paramount in metal stamping, and quality control measures are in place at every stage. Modern stamping machines often incorporate sensors and automation to monitor and adjust the process in real-time, ensuring each stamped component meets stringent quality standards. The Pivotal Role of Metal Stamping Die in Manufacturing Metal stamping die plays a pivotal role in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, and more. Its importance lies in its ability to produce consistent, high-quality components with incredible precision. Here are some key areas where metal stamping die shines: Mass Production: Metal stamping die enables the mass production of components with minimal variation. This is crucial in industries where large quantities of identical parts are needed. Cost Efficiency: The efficiency of the stamping process, coupled with the durability of the dies, contributes to cost savings in production. Complex Shapes: Metal stamping can produce components with intricate shapes that would be challenging or impossible to achieve through other manufacturing methods. Material Utilization: Stamping optimizes material usage, minimizing waste and making it an eco-friendly manufacturing method. Consistency: The precision of metal stamping die ensures that each component is virtually identical, reducing the risk of defects and improving product performance. In conclusion, metal stamping die is a testament to the marriage of artistry and science in manufacturing. Its evolution from humble beginnings to its pivotal role in modern industry showcases the relentless pursuit of precision and efficiency. As technology continues to advance, metal stamping die will undoubtedly remain a cornerstone of manufacturing, enabling us to turn sheets of metal into the intricate components that power our world.