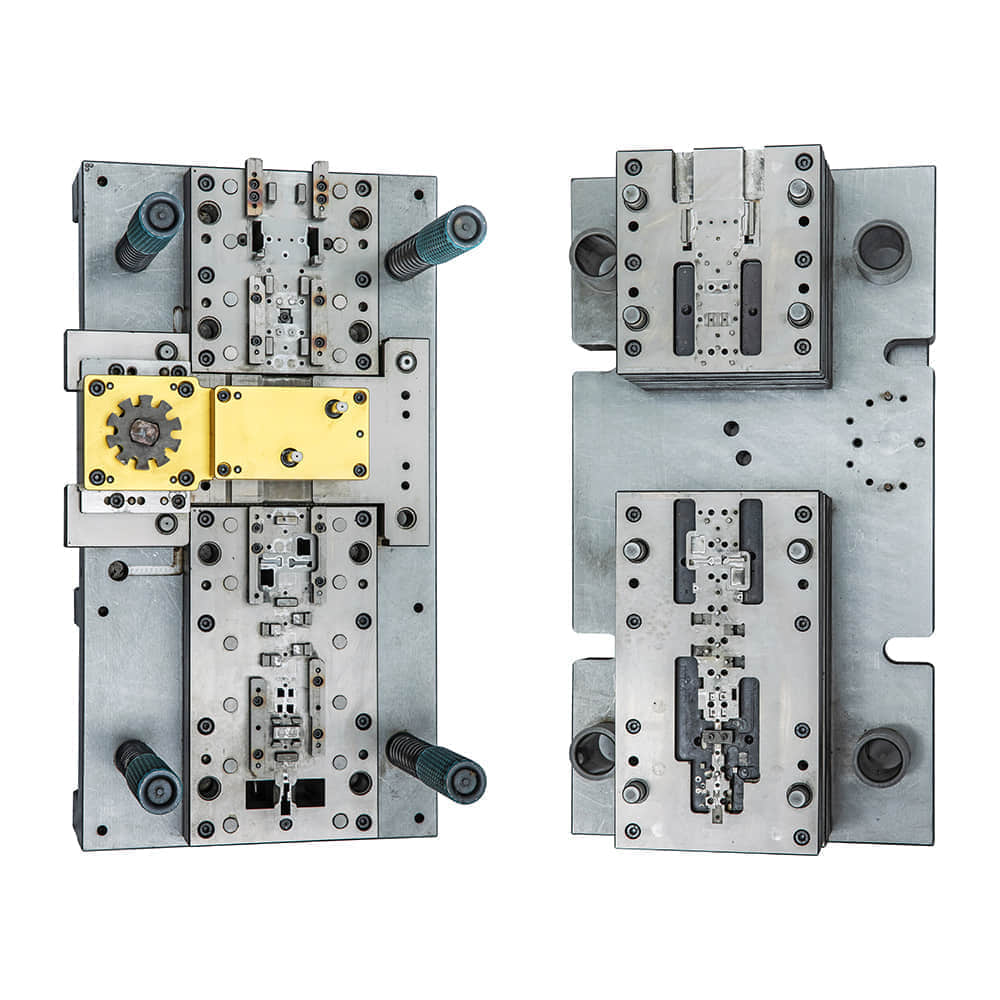
Metal stamping die, a crucial tool in the manufacturing industry, holds a pivotal role in the production of precision metal components. This article aims to delve into the intricacies of metal stamping die, exploring its construction, working principles, and diverse applications across various industries.
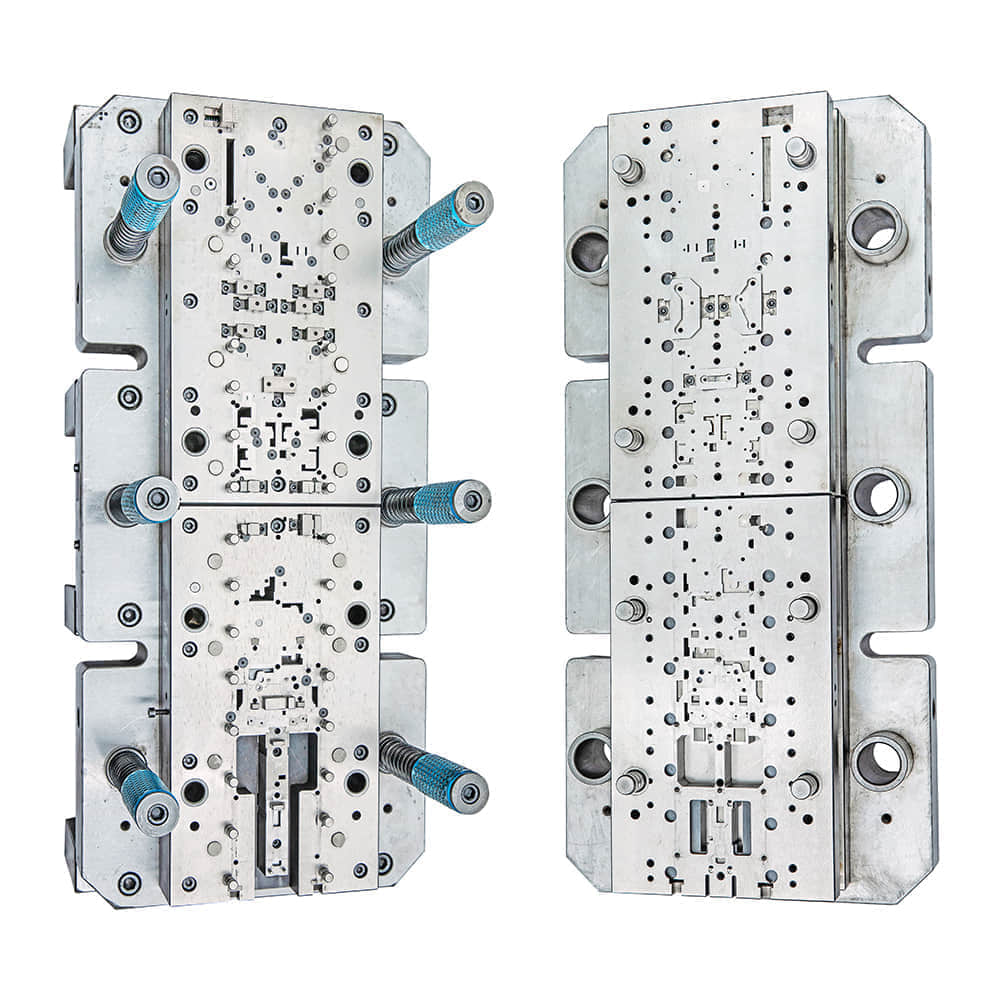
At its core, a metal stamping die is a specialized tool designed to shape and form metal into desired shapes and sizes. It consists of two main parts: the upper die and the lower die. When the metal sheet or strip is placed between these two dies and subjected to compressive force, the metal deforms and takes the shape defined by the die cavity. The precision and quality of the stamped product largely depend on the design and quality of the stamping die.
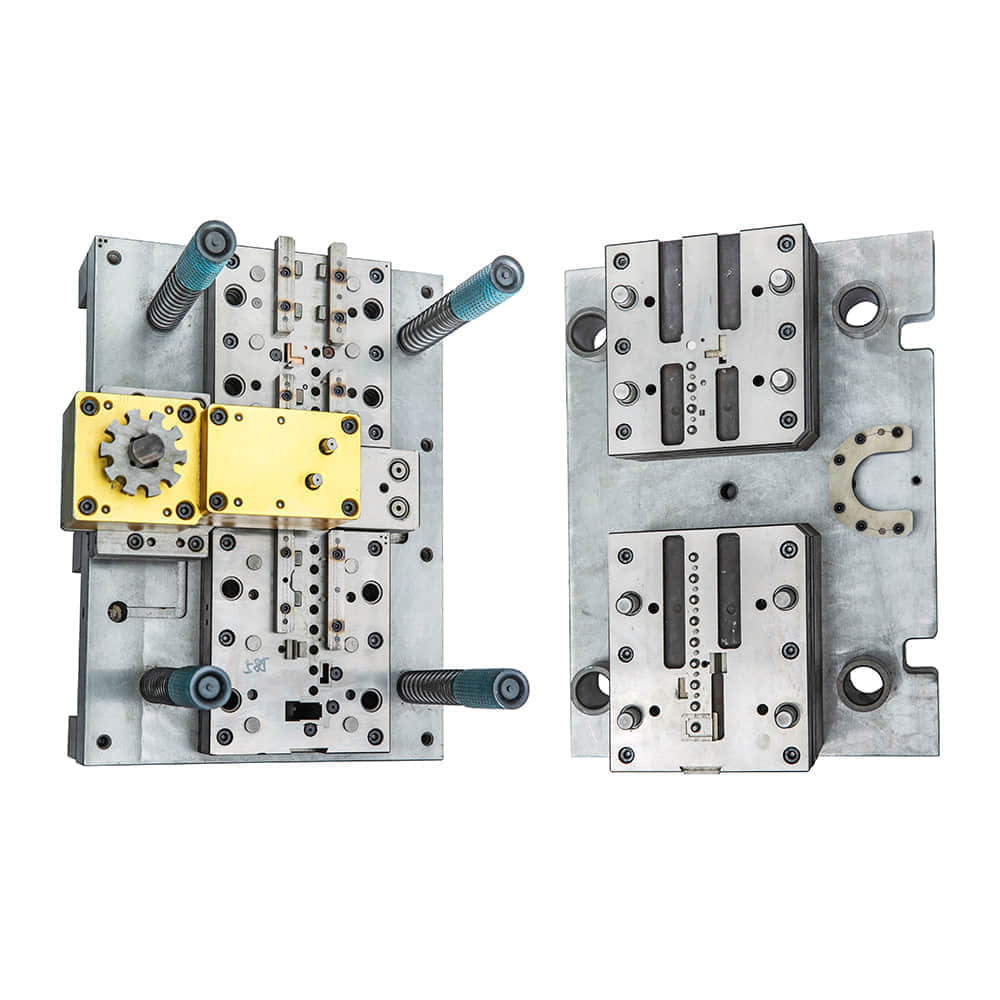
The construction of a metal stamping die involves intricate engineering. It must be able to withstand the significant forces exerted during the stamping process while maintaining precise tolerances. Materials such as tool steel, carbide, and ceramics are commonly used for die manufacturing due to their high hardness, wear resistance, and dimensional stability. The die’s surface finish and geometry are also carefully controlled to ensure smooth metal flow and avoid defects like cracking or wrinkling. The working principle of metal stamping die relies on the principles of plastic deformation. When the metal is compressed between the dies, it undergoes plastic deformation, which means it permanently changes its shape. The degree of deformation depends on factors such as the metal’s properties, die design, and stamping speed. By carefully controlling these parameters, manufacturers can achieve precise and repeatable results.